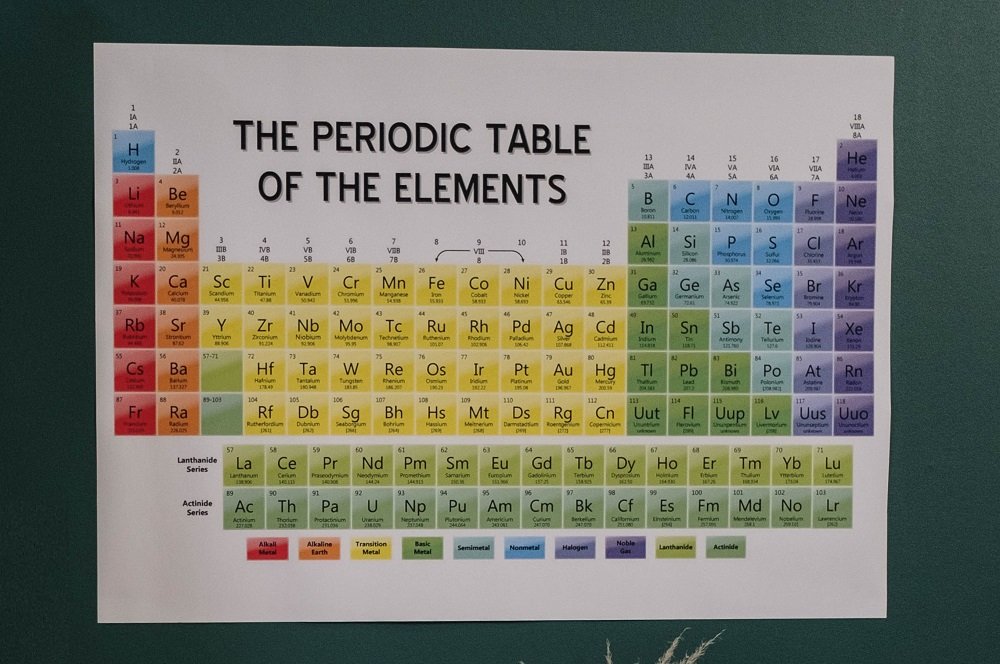
Group Vs. Period: 7 Key Differences
One of the core terms that chemistry revolves around is the periodic table, and students are constantly faced with the task to understand and memorize period and group element of the periodic table all the time by their professors and teachers.
While many students try to learn it as a part of the syllabus, the genuine concept of the periodic table can only be understood once we understand the difference between group and period.
So, follow along as we take a deeper look into period vs. group debate, as they are the supporting pillars that make up the entire periodic table.
Period vs Group Periodic Table: A Brief Overview
The main difference between group and period is their position and arrangement in the periodic table. If you look into the periodic table, you can find that groups are arranged in a horizontal position, while on the other hand, periods are arranged in a vertical position.
And although they oppose each other by their arrangements and definition, both serve the purpose of arranging all known elements with proper order so that we can find them easily and efficiently.
Also, for anyone interested in science, learning the differences between groups and periods is vital, as there is always a chance of a new element to join the ranks of the periodic table.
If you consider yourself a true connoisseur of chemistry, then it is vital that you learn about the differences between groups and periods.
What Is Group?
In general terms, a group on a periodic table is represented as the vertical columns that host elements with identical electron configuration but tends to change the nature of the elements from left to right. In total, there are 18 groups in a periodic table.
Each of these groups has an individual name, and the groups are named due to their nature and reactions to other elements. The names of the groups are:
- Group 1: Alkali Group
- Group 2: Beryllium or Alkaline Earth Metal Group
- Group 3: Scandium Group
- Group 4: Titanium Group
- Group 5: Vanadium Group
- Group 6: Chromium Titanium Group
- Group 7: Manganese Group
- Group 8: Iron Group
- Group 9: Cobalt or Coinage Metal Group
- Group 10: Nickel Group
- Group 11: Copper or Coinage Metal Group
- Group 12: Zinc or Volatile Metal Group
- Group 13: Boron or Icosagens Group
- Group 14: Carbon Group
- Group 15: Pentels or Nitrogen Group
- Group 16: Chalcogens or Oxygen Group
- Group 17: Halogens or Florine Group
- Group 18: Noble Gases or Neon Group
All currently known elements are divided into one of these 18 groups. Each group of elements has different nature and attributes. For example, the Neon or the Noble Gases group consists of elements that completely fills their octet and is in the utmost stable form.
What Is Period?
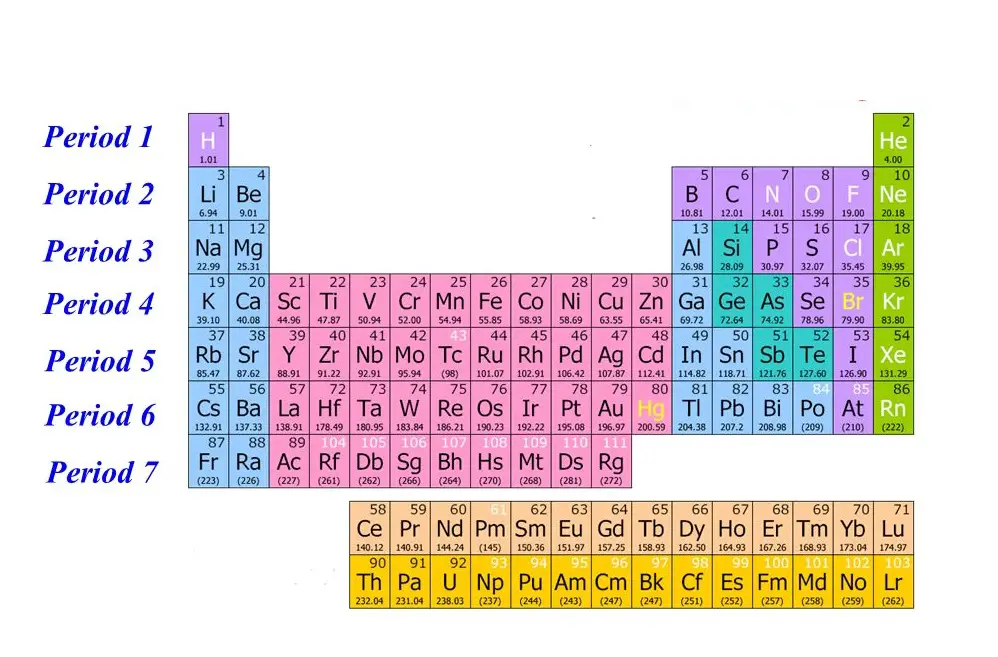
Period refers to the 7 horizontal columns on the periodic table and every period from left to right expands to a new electron shell.
Starting from hydrogen all the way up to the seventh-period francium, the elements will increase their orbitals, meaning the electrons of the elements will represent a gradual increase in energy or power level.
So, for example, lithium has two power shells as it is in the 2nd period, but at the same time, potassium has four power shells because it is in the 4th period. And this rule applies to all the elements incorporated within the periodic table.
Another interesting fact regarding period is that, although all the periods contain 18 groups, period 6 and 7 include a total amount of 32 groups.
Learn The Difference Between Grammar and Syntax
Main & Core Differences Between Group and Period
Now, here are the core differences between groups and periods on a periodic table:
Position
The positions of the groups are in vertical order, while the positions of the periods are in horizontal order on a periodic table.
Total Numbers
There are a total of 18 groups on the periodic table, while there are currently 7 periods on the periodic table. Now, while some may want to include the lanthanide and actinide series, they are just parts of periods 6 and 7.
Properties
In groups, all the elements share identical properties, but in periods, none of the elements share the same type of properties whatsoever.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity increases from the bottom to the top for groups, but for periods, electronegativity increases from the left to the right.
Size of the Atoms
In groups, the size of the atoms increases gradually from top to bottom but in periods, that happens from left to right.
Electron Configuration
The electron configuration stays the same for groups, but that’s not the same for periods as the electron configuration gradually changes for periods from left to right.
Electron Shells
For groups, the number of electron shells increases as you go from the top to the bottom, but for periods, no change occurs as the electron shells of the periods always stay the same.
Some of Our Articles You May Want to Read:
- Difference Between Table and Chart: A Comparative Guide
- Systematic Review and Literature Review: What’s The Differences
- Difference Between Mean, Median, and Average
Group Vs Period: The Comparison Table
|
Parameter of Comparison |
Group |
Period |
| Definition | There are vertical columns of elements in a periodic table that gradually increase their atomic size from top to bottom, and these columns are called groups. | There are horizontal rows of elements in a periodic table that gradually increase their ionic numbers from left to the right, and these rows are called periods. |
| Total Numbers | There are 18 groups in the modern periodic table. | There are 7 periods in the latest periodic table. |
| Electronegativity | The electronegativity of a group increases from the bottom to the top and vice versa. | The electronegativity of a period increases from the left to the right and vice versa. |
| Similarity in Properties | Every element on a group shares similar attributes and properties, and although they are not identically the same, there are only a few changes here and there. | On the other hand, elements on a period don’t share any sort of similarities when it comes to properties and attributes. Only a few may share some familiarities, but even that occurs in special conditions; won’t occur naturally. |
| Electron Configuration | The electron configuration of a group stays the same, as elements of the same group contains the same number of electrons in their very last shell. | The electron configuration for periods increases from left to right in a consistent manner, and this also ensures that the energy level of the atoms also amps up. |
| Valance of Elements | The valance of the elements on a group remains equal and doesn’t change unless extreme conditions are applied. | The valance of the elements on a period increases first till group IV but then starts to decrease until group O. |
| Size of the Atoms | The size of the atoms increases from the top to the bottom. | The size of the atoms gradually increases from left to right. |
| Number of Shells | Electron shells differ from each element on a group; the number of the shell increases from the top to the bottom. | All the elements in a period have the same number of electron shells. |
Key Takeaways
- Groups and periods are the base of the periodic table.
- There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the periodic table.
- Electronegativity drops down when you go from top to bottom of a group, while electronegativity amps up when you go from the left to the right of a period.
- Elements on a group follow the same type of elements and cause similar reactions with other elements, while elements in a period contain different types of elements and characteristics.
- Elements on a group have identical electron configuration, while elements on a period have an equal amount of valence electrons.
Conclusion
If you want to maneuver through the periodic table and gain complete mastery of it, then there is no other way than to understand the true concepts of period vs group.
Because unless you know the difference between group and period, you can’t identify the elements properly, and your journey to the world of chemistry will be a fool’s errand. Therefore, understanding groups vs periods should be one of your top priorities!