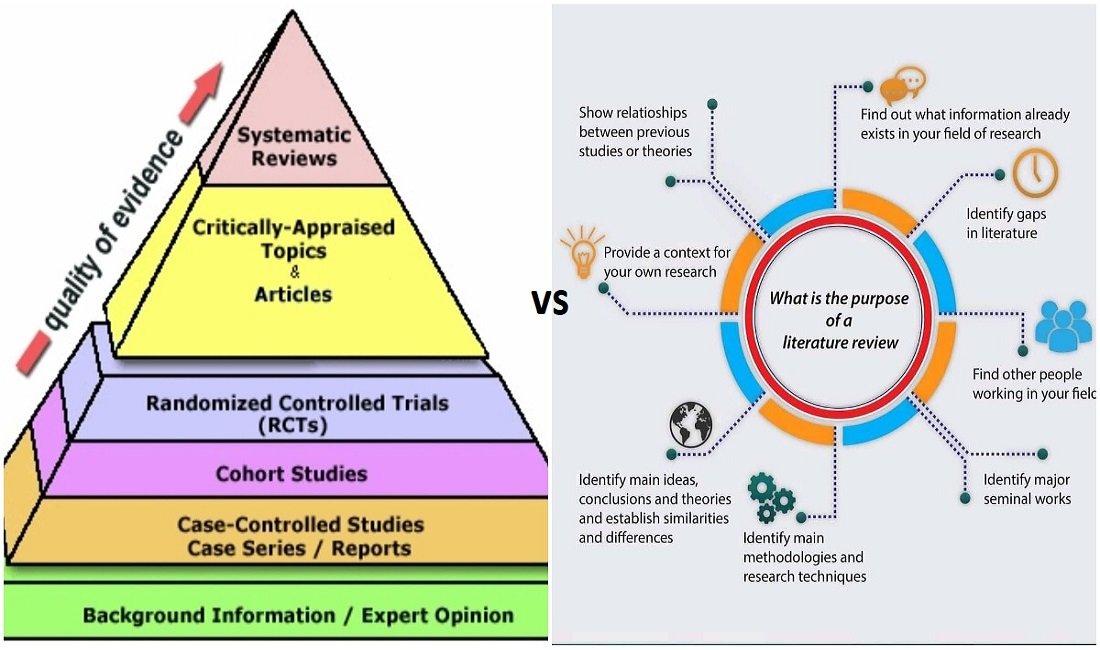
Systematic Review and Literature Review: What’s The Differences?
Systematic and literature reviews are used to give a piece of summary information; both reviews also synthesize evidence. So what is the difference between systematic review and literature review?
In a scenario in which a battle between the two arises, which one should you go for? Both are used to summarize information, data, research, or literature that already exists.
Although they are quite similar patterns, they are used to review or summarize information with different kinds of perspectives. When used properly, they can add a lot of value to your research.
So, here in this systematic review vs literature review comparison piece, we’ve given you all that you need to know about these review types and where you should use them.
Systematic Review
The first thing that you need to know about systematic reviews is that it tackles a clearly formulated and constructed question. So it is more organized and to the point. For example, the review could be about the effectiveness of treatment. There is research and statistics in this sort of research rather than thoughts and opinions.
To review or answer this question in a way, the review pattern uses reproducible, and as the name suggests, systematic methods.
In short, the evidence against or for the question at hand is summarized. Relevant research that can be brought to the table for this review is then found, assessed, and selected in this way.
A similar tactic is then followed to analyze and collect information that might be of use in the review form of the selected research.
The Process of Systematic Reviews
Here is how you would get a systematic review started, described in steps.
Step 1: Set Protocol
To start things off, you get to set a plan or protocol. You need to build a team of researchers that are familiar with the topic that you must review.
Step 2: Get the Research Started
Designated review teams will go through studies with a sensitive and productive search strategy.
Step 3: Screen the Research
All the research that the teams select must be screened thoroughly to see relevancy and usefulness; this is where you decide whether or not the studies are eligible to be used in the review.
Usually, another team does the screening process using the inclusion and exclusion criteria. It’s best if this part is done by two independent people. That way one’s opinion is not influenced by the other.
Step 4: Extraction
You can’t use the whole study or research paper for your review. Usually, there is information here that your review could do without. So now it is time to extract all the information that is of actual use to your review.
Step 5: Present Data
All the data that you have extracted now has to be presented in order. Synthesize the extracted data and place them in relevant spots. To do this, you can either use meta-analysis or narrative synthesis.
Descriptive Vs. Inferential Statistics: The Main Differences?
Literature Review

Literature reviews are mostly used to review books or published articles. It focuses on work that has been previously published. You might also know this kind of review style as narrative reviews.
In the literature review, you get an overview or an idea about a particular topic that an author has decided to write about. Usually, the information presented in this sort of literature is previously known.
But, the literature review does not just state what an article or book states; the review assesses and evaluates it.
Unlike a systematic review, the literature review does not use any pre-specified protocol or plan. Methods used or how the review is being conducted are usually not stated in a review of this sort. There is also no set way or method that you need to follow for the review.
Reviews as such have a comprehensive but not exhaustive approach.
One thing that you will see in a narrative review is a thorough discussion. Using a topical approach, precision is never on top of the list when conducting this sort of analysis. So the data is not replicable.
Writers often express their takes on the subject matter.
When to Use Literature Reviews
Here is where you would commonly find literature reviews:
- Academic research
- Book reviews
- Reviews of articles
Recommended for You:
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources – The Differences You Must Know
- Qualitative Vs. Quantitative – What’s The Difference?
- Parameter Vs. Statistic: What Are The Differences?
Systematic Review Vs Literature Review: The Comparison Table
To better understand the two types of reviews, we thought it would be better to use a side-by-side comparison.
|
Parameter |
Systematic Reviews |
Literature Reviews |
|
Basic Definition |
Review of focused questions by assessing, synthesizing, identifying, and selecting appropriate studies. |
Interpretation of studies or articles using a qualitative approach and subjective guidelines. |
|
Main Objective |
Answer and discuss topics that have straight answers, such as clinical discussions with no biases. |
Summarize literature and articles that include self-opinion as a general overview. |
|
Common Topics |
Topics that have clear conclusions can be reached through the support of data and statistics. |
Can be any general topic, an article, or a book. |
|
Contents |
Systematic research, inclusion and exclusion criteria of studies in the review, research strategy, validity or relevance of studies used, interpretation and conclusion of the research and references. |
Introduction, sometimes method that is to be followed, analysis, opinions, comparisons, conclusion, and references. |
|
Time Needed to Complete Review |
Usually takes months or even years to reach a dependable conclusion. | Might take weeks or months. |
|
Number of People Per Review |
Group of three or more, depending on the research team. |
Can be done by one or two people. |
|
Requirement |
Through understanding of the topic with relevant studies as backup and statistical analysis. |
Basic understanding of the article or literature. |
Key Takeaways
- Systematic Review is based on research, studies, and evidence
- There are no inclusion or exclusion criteria used in literature reviews
- You need a specific guideline or protocol for systematic reviews
- Conclusions in literature reviews almost always include the writer’s opinion
- No statistical information is used in literature reviews
- Conclusions reached in systematic reviews are rarely biased and rely highly on evidence
Final Words
Different topics have different approaches when it comes to writing reviews. It becomes quite difficult to get your message through without the help of the right review format.
These review techniques have evolved over time and can sometimes influence each other a little bit. So it’s normal to get confused between the two. Hopefully, this systematic review vs literature review was able to help you understand where they are applicable.