Hepatitis A, B and C – What Are The Differences?
Hepatitis comes in three different forms: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C. Most people do not fully understand the difference between the three forms and their symptoms can be similar. Blood tests can determine which form you have when diagnosed with hepatitis.
How is Hepatitis Spread?
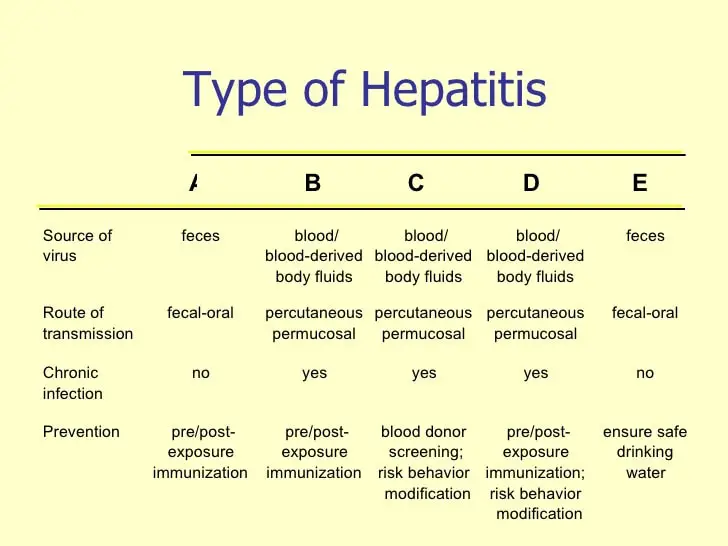
Hepatitis A or HAV is spread through close personal contact. It can be spread through sex, eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water. People living in the same household as an infected person are at a high risk.
Hepatitis B or HBV is found in blood and some bodily fluids. HBV is spread when you come into contact with contaminated blood or bodily fluids. It is spread through unprotected sex, sharing drug needles or from an infected mother to her child.
Hepatitis C or HCV is also found in blood and some bodily fluids. It is spread through sharing needles, exposure to needlesticks or sharps on the job and in some instance through an infected mother to her child. Although not common, it is possible to transmit HCV during sexual intercourse.
AIDS vs. HIV – 5 Differences You Should Know
Who Should Be Vaccinated?
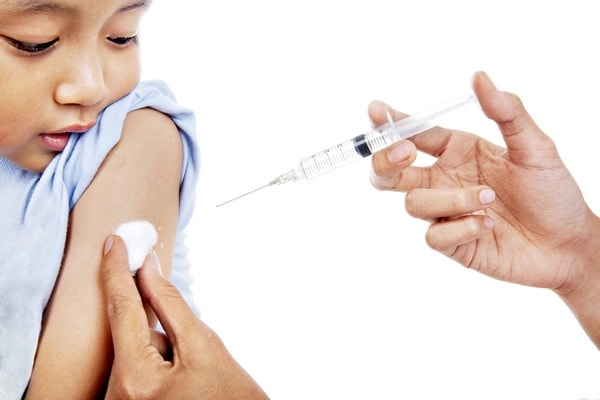
HAV does have a vaccination available to prevent the infection from occurring. All children who are 12 to 23 months old, homosexual men, users of street drugs and people who travel to third world countries should have the vaccine. People who have clotting disorders such as hemophilia should also have the vaccine.
HBV also has a vaccination that is available and all infants, children and teens between the ages of 0 to 18 years should be vaccinated. Sexually active people should also be vaccinated and also homosexual men. Health care workers and public safety workers will also need the vaccine.
There is no vaccination for HCV.
Incubation Period
HAV has an incubation period of 15 to 50 days, usually averaging 28 days. HBV has an incubation period of 60 to 150 days, usually averaging 90 days. HCV has an incubation period of 14 to 180 days, usually averaging 45 days.
Treatment
- HAV has no treatment options. Supportive care can be given and avoidance of alcohol since it can make liver damage worse.
- HBV patients will need to have medical exams every 6 to 12 months to check for liver disease. There are also several antiviral medications that are available for those diagnosed with HBV.
- People with HVC will need to do medical exams every 6 to 12 months checking for liver disease. There are medications available for those suffering from chronic HCV.
Recommended for You:
Differences Among Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C
Let’s discuss all the differences in a nutshell. See the below Hepatitis A vs Hepatitis B vs Hepatitis C comparison chart.
Hepatitis A |
Hepatitis B |
Hepatitis C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|