Stroke Vs. Heart Attack: What Are The Main Differences?
Many people confuse the two terms and even think they’re just two names for the same problem, but there’s a huge difference between stroke and heart attack. Both conditions are dangerous and even potentially deadly.
They may even have some similar symptoms, but they affect two distinct organs, and their management is different too. Let’s have a closer look at strokes and heart attacks to see exactly what they entail.
Stroke
A stroke happens when something blocks or hinders the blood flow to the brain, resulting in cell death. Usually, it’s a blood clot blocking an artery that supplies the organ with blood. There are two main stroke types: hemorrhagic, caused by bleeding, and ischemic, caused by poor or lack of blood flow.
The symptoms of a stroke can include problems speaking or understanding, inability to move or weakness in one side of the body, numbness in one side of the body, facial weakness, blurred vision, sudden headache, or confusion. The symptoms rarely include pain and usually occur soon after the stroke took place.
The main risk factors that can lead to a stroke are high blood pressure, obesity, smoking, high cholesterol, atrial fibrillation and diabetes mellitus. Management differs depending on the type of stroke and may include aspirin administration, tight blood sugar control, surgery (neurosurgical intervention, thrombectomy), and others.
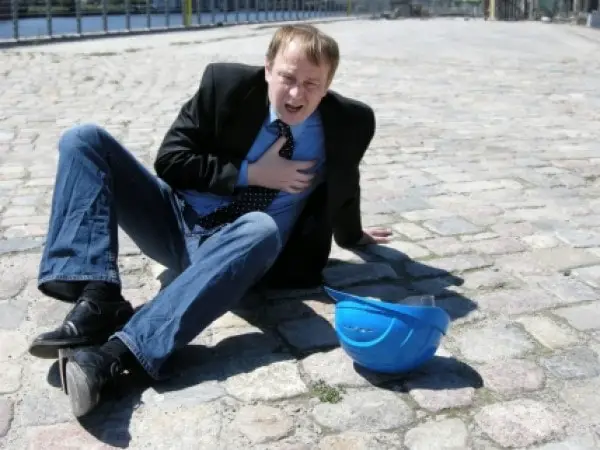
Heart Attack
A heart attack, or a myocardial infarction by its scientific name, happens when lack of blood flow to the heart produces damage to its muscle.
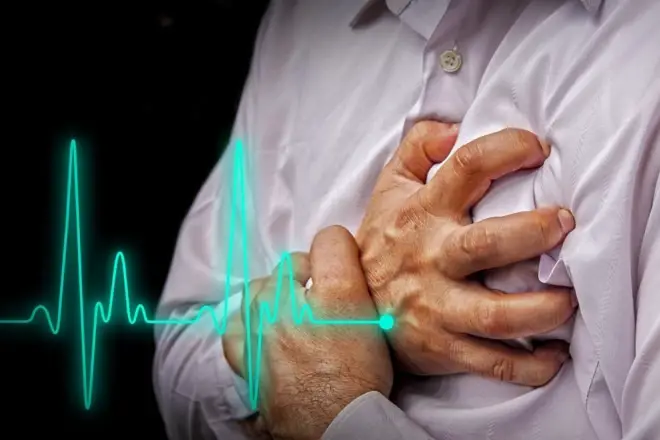
Similarly to the case of a stroke, it can happen when a blood clot in an artery that “feeds” the heart blocks blood flow, causing the muscle to “starve”, which results in chest pain and other symptoms, shortness of breath, nausea, severe pain in the arm, jaw, neck, or even the stomach and back. If you are confused between artery and vein have a look at our artery vs vein article.
Other signs that may accompany the main symptoms include a feeling of light-headedness, nausea, vomiting, and excessive sweating. As for management, it may include percutaneous coronary intervention, thrombolysis, cardiac rehabilitation, beta blocker medication, targeted temperature management, aspirin, eptifibatide, and others.
Heartburn vs. Acid Reflux: How They Differ?
The Differences between Stroke and Heart Attack
Now that you have a better understanding of the conditions, let’s put them side by side to see what makes the difference between stroke and heart attack. Check out the table below:
Stroke |
Heart Attack |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note that, even if you know the differences between heart attacks and strokes, the vital thing you must always do at any sign of the conditions is to call an ambulance. For more useful articles on medicine, biology, science or even IT and philosophy, subscribe to our newsletter.