Difference Between Signs and Symptoms
Medical terms can be very confusing, and one such pair is sign and symptom. Many people don’t even know the literal meaning of these but only know what’s implied.
Today, we’ll discuss the difference between signs and symptoms, along with their literal meaning.
Sign vs. Symptom: A Brief Overview
The words sign and symptom can be used to address medical abnormalities, but they aren’t used interchangeably in the medical sector.
In the medical sector, signs are health conditions or issues that can be observed. For example, a patch of rash on your skin or the wheezing sound of your breathing can be termed as signs.
On the other hand, symptoms are health issues that professionals can’t observe. For example, if you’re feeling a throbbing pain at the back of your head, that would be a symptom because no one can observe that.
What Is Sign?
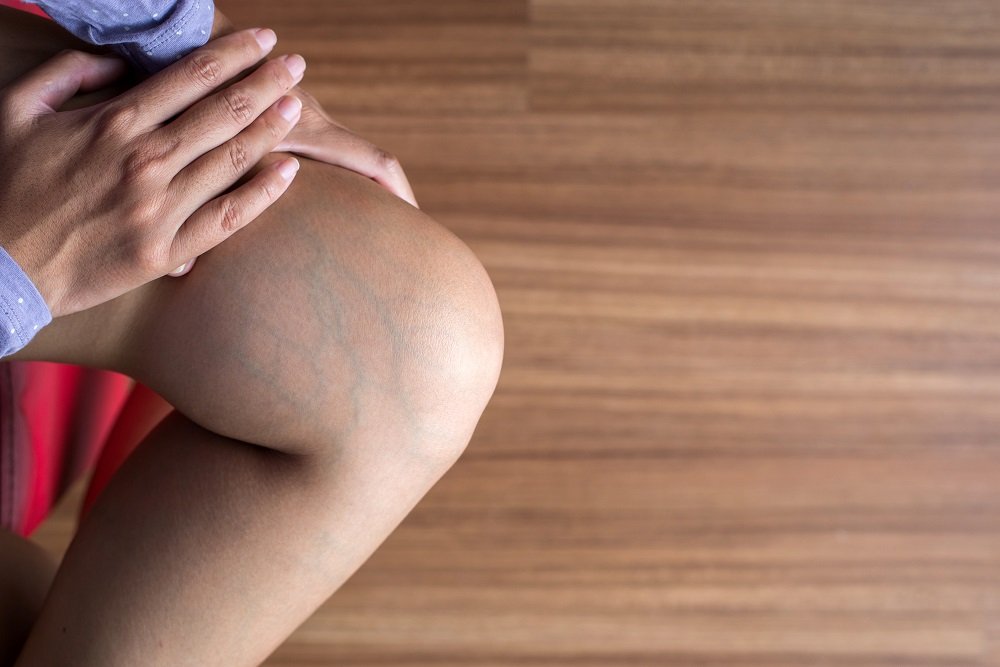
In medical terminology, signs are health conditions that can be observed directly. Signs are much more reliable than symptoms because it’s easier to determine the cause behind the effect.
Some of the most important signs in the medical sector are heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, temperature. These are known as vital signs.
There are four types of signs in pathology. These are:
- Diagnostic Signs
Diagnostic signs are the ones that can help a doctor pinpoint the cause of a problem.
- Anamnestic Signs
These signs indicate past medical records. For example, a person with visible paralysis on their face is likely to have suffered from a stroke.
- Prognostic Signs
Prognostic signs indicate prognosis, which is an outcome that can be predicted for a specific patient. For example, a breast cancer lump can be observed to determine the possible survival rate of the patient.
- Pathognomic Signs
Pathognomic signs are like diagnostic signs, but these offer a higher possibility.
What Is Symptom?

Unlike signs, symptoms are medical health issues that can’t be observed. The experiences of patients are widely categorized as symptoms because they can’t be seen. For example, a doctor can’t see the pain of his patients.
The three types of symptoms are:
- Chronic Symptoms
Chronic symptoms are symptoms that recur over a long period. For example, in a patient suffering from heart disease, chest pain, palpitation, etc., can be chronic symptoms.
- Relapsing Symptoms
Relapsing symptoms are symptoms that were considered to be resolved but are back. Depression is one of the most common relapsing symptoms.
- Remitting Symptoms
If a symptom reduces or disappears over time, then it’ll be a remitting symptom. For example, if the symptoms of migraine reduce over time, it’ll be considered as remitting symptom.
Major Differences Between Medicare and Medicaid
Difference Between Signs and Symptoms
As we’ve already discussed, there is a lot of difference between signs vs. symptoms. In this section, we’ll discuss the key differences.
Nature
Signs are objective evidence of health conditions that can help diagnose a certain problem. Symptoms are subjective evidence of health conditions, or more precisely, indications of health conditions.
Visibility
Signs are visible. For example, rash on the skin can be observed. However, symptoms aren’t visible, like headache or nausea.
Detectability
Signs can be detected by anyone who can take a look at the patient. However, symptoms can be seen and experienced by the patient only.
Verification
The patient can verify signs if he’s knowledgeable enough. However, symptoms may require a thorough checkup by physicians to detect the actual cause.
Recommended for You:
- Difference Between Counseling and Psychotherapy
- Heartburn vs. Acid Reflux: How They Differ?
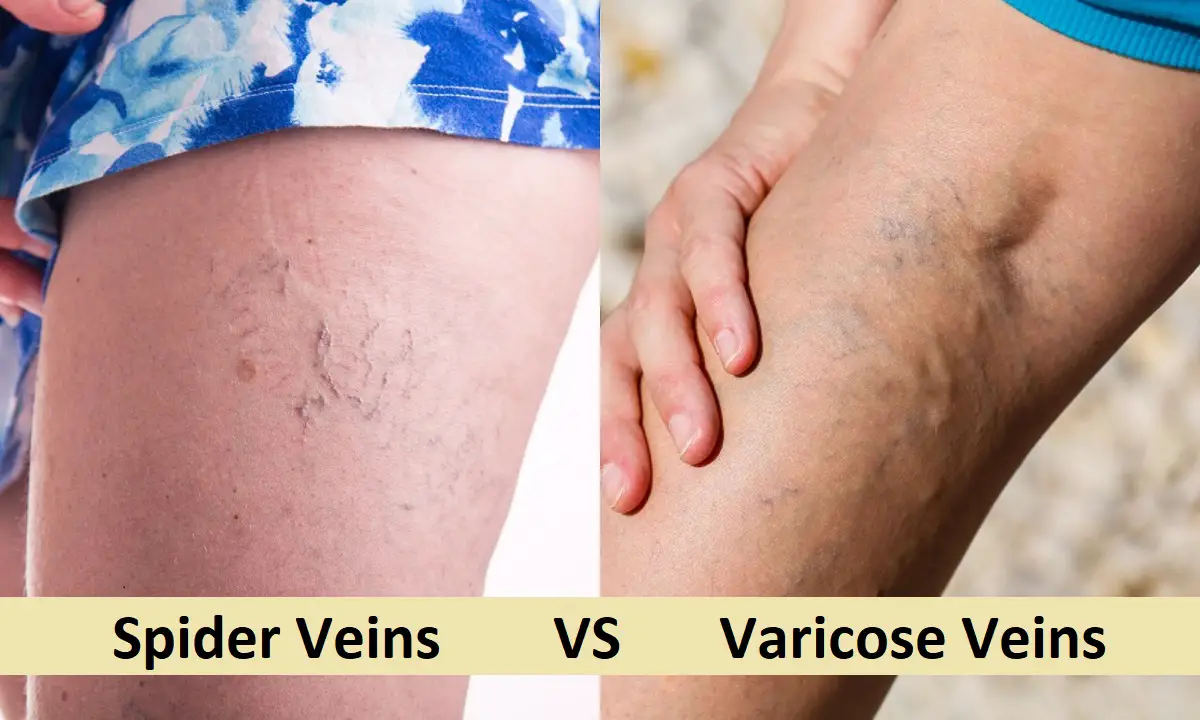
- Difference Between Spider Veins and Varicose Veins
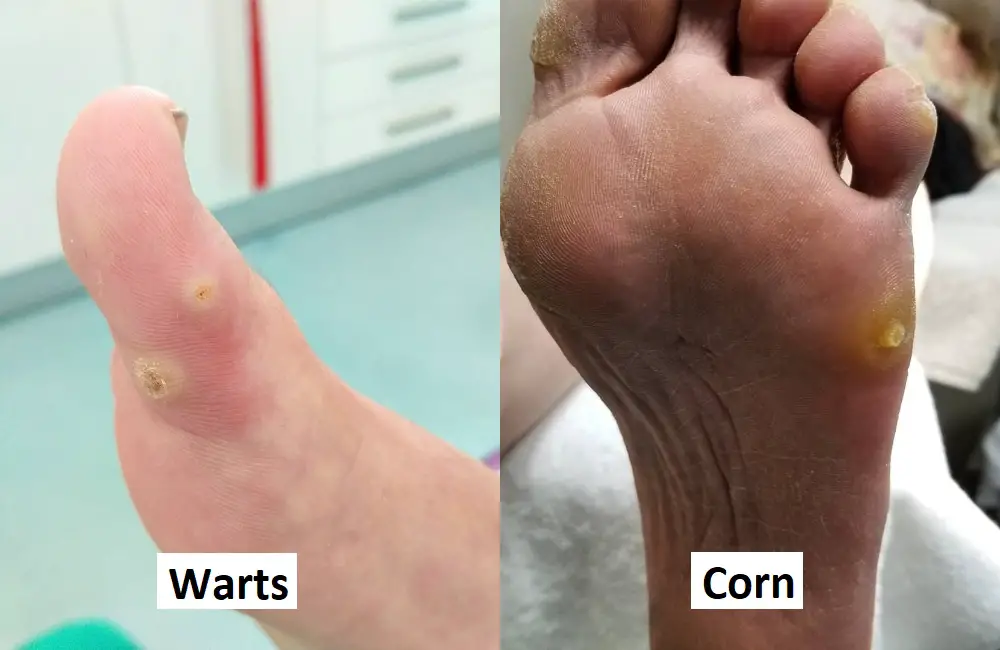
- Difference Between Corn and Wart
Sign vs. Symptom: The Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Sign | Symptom |
| Definition | In medical terminology, signs are health conditions that can be observed. | Symptoms are medical health issues that can’t be observed. |
| Nature | Objective evidence | Subjective evidence |
| Visibility | Visible | Invisible to the five senses |
| Verification | It can be verified even by patients | Verification is not possible without a thorough checkup |
| Detectability | Anyone can detect it | Only the patient can feel or experience it |
| Measurability | Tools such as stethoscope, X-ray imaging, thermometer, etc. are used to determine these | It can’t be determined using any tools. |
Key Takeaways
- Signs are objective evidence of a health condition.
- Symptoms are subjective evidence of a health condition.
- Signs are visible and can be detected by anyone.
- Symptoms aren’t visible and require a physician to determine what’s causing it.
Conclusion
As you can see from our sign vs. symptom guide, signs and symptoms aren’t the same terms, even though they are used interchangeably. These are important to know for working in the medical sector or for understanding medical papers.