5 Differences Between RAM and ROM
Unless you’re into IT, it can be quite difficult to understand everything about how a computer works and stores data, even though you’re using a device every day. Every computer needs memory to operate and you will probably have heard the terms RAM and RAM.
You might even know what they stand for but answering the question how are RAM and ROM different might not be so easy. Let’s analyze both types of memory in detail, to see what they’re all about. Let’s get started!
RAM

RAM, short for ‘Random-Access Memory’, is a type of data storage used for holding program instructions that are frequently used, with the purpose of increasing the system’s general speed. RAM devices allow data to be written and read fast, requiring almost the same period of time regardless of where the data is located inside the memory.
Basically, RAM is used to store temporary data created and used by computer programs and requires a flow of electricity to retain that information. Therefore, when you turn off your computer, the data held in RAM will be lost.
This is what it’s called a “volatile memory”. Efforts have been made to create non-volatile RAM devices, and there are types of memory that can retain data even if power is removed (ROM included), but they all have limitations.
SDHC Vs. SDXC: What Are The Main Differences?
ROM

ROM, short for ‘Read-Only Memory’, is a non-volatile memory that cannot be altered or reprogrammed easily (hence the name). Data stored in ROM is not lost when power is removed, but writing on a ROM chip is painfully slow.
Usually, such memory is used for data that is closely linked to various hardware components and is unlikely to require regular updates.
One example of ROM is the BIOS in your PC – a chip that holds the instructions needed for your computer to begin the initial start-up process.
What is the Single Most Crucial difference between RAM and ROM?
– The main difference between RAM and ROM is their volatility.
The Differences between RAM and ROM
Now that you know a bit more about the two types of memory, let’s see exactly what the difference between RAM and ROM is. Check out the table showing RAM vs ROM for a straightforward comparison.
RAM |
ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recommended for You:
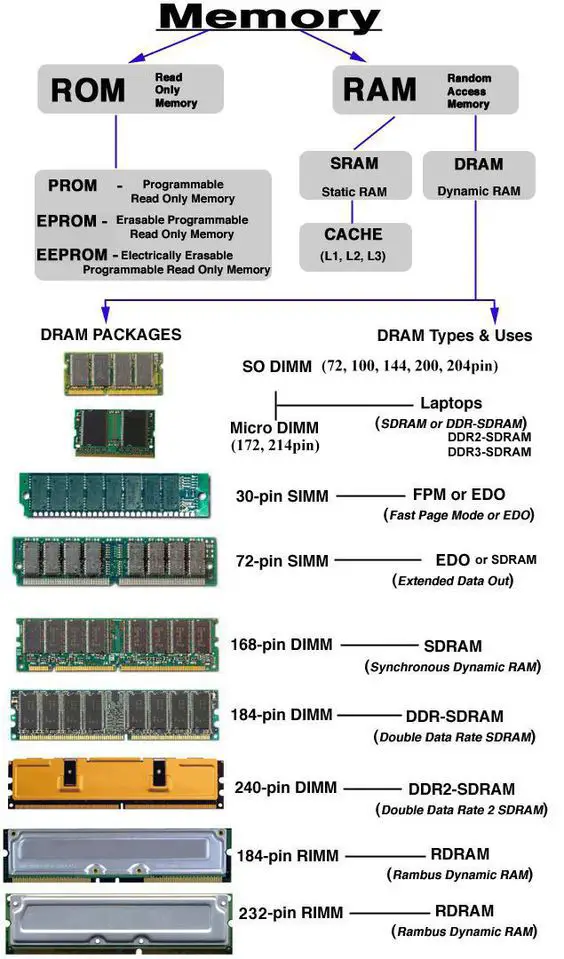
RAM and ROM infographic:
Liked our post on the difference between ROM and RAM? Subscribe to our newsletter and we’ll send you useful articles on a variety of topics, from IT and science to business, economics and even philosophy!